
Lewitt announce drum microphone kits
The Beatkit and Beatkit Pro are complete drum microphone kits aimed at both live sound and recording applications.

The Beatkit and Beatkit Pro are complete drum microphone kits aimed at both live sound and recording applications.

V16 of Melda Production's plug-in range allow them to benefit from the power offered by modern computer systems.

The Pro-Audio Show 22 is a new UK show coordinated by the IPS (Institute of Professional Sound) and dedicated to professional audio equipment.

A set of 16 original Neve 1057 microphone preamp and EQ modules originally installed in the first Neve 80 Series console have been put up for auction.

Sonokinetic are currently running a sale offering large discounts across their range of sample libraries and virtual instruments.

The LS-P5 recorder from OM System features an upgraded microphone system and Bluetooth remote control facilities.

Made entirely from multi-sampled synths, Synth AI promises "a modern fusion of cinematic synthesis."

Mercury from Spitfire Audio samples a collection of unique instruments built by Chas Smith, a builder whose creations have featured in the work of some of the world's top composers.

EastWest's summer sale offers discounts of up to 60% across their entire product range, and up to 45% off of ComposerCloud subscriptions.
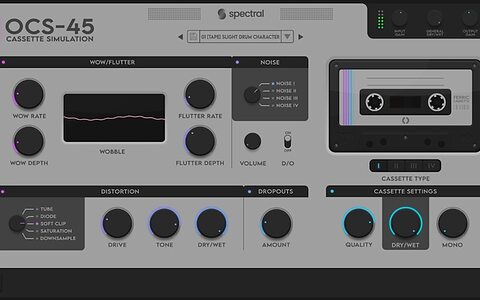
Spectral Plugins have released OCS-45, a cassette tape simulation plug-in that offers a variety of lo-fi sounds and creative distortion effects.