
Cherry Audio Mercury-4 softsynth
Software synth devs release virtual version of Roland's classic Jupiter-4.

Software synth devs release virtual version of Roland's classic Jupiter-4.

Who wouldn't want to win this stunning Thunderbolt 3 audio interface plus every single Real Time FX processor (50+) in the Antelope Audio collection? (Prize worth €4000$4000.)

Casio claim that their newest Privia series digital pianos are the world's slimmest 88-note hammer-action keyboards.

PMC's latest studio speakers employ a number of proprietary technologies, including the company's trademark Advanced Transmission Line bass loading.

Buchla USA and Tiptop Audio have teamed up to build a faithful recreation of the classic West Coast synth, in Eurorack format.

Percussion powerhouse incorporates four synth voices, a four-track step sequencer, a mixer, an analogue delay and an optical bus compressor.

New reverb plug-in offers a selection of small and quirky room simulations.

New bundle comprises three Moog modules plus accessories, a dust cover and a card game.

The Beatmaker Bundle and Recording Bundle include everything you need to start making music.
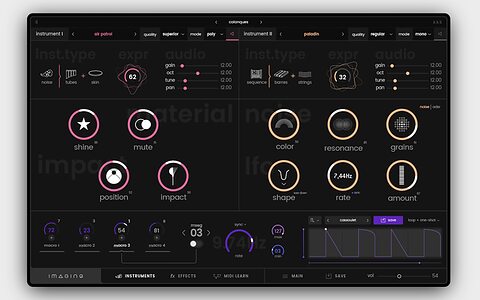
New software instrument uses real-world acoustic principles to create otherworldy sounds.